You are more likely to develop gestational diabetes if you have any of the following risk factors
Previous gestational diabetes;
Gestational diabetes often starts in the middle or towards the end of pregnancy because this is when the levels of pregnancy hormones are very high. Pregnancy hormones can cause a rise in blood sugar.
Gestational diabetes is very common and it affects up to 18 in 100 women during pregnancy.
You are more likely to develop gestational diabetes if you have any of the following risk factors
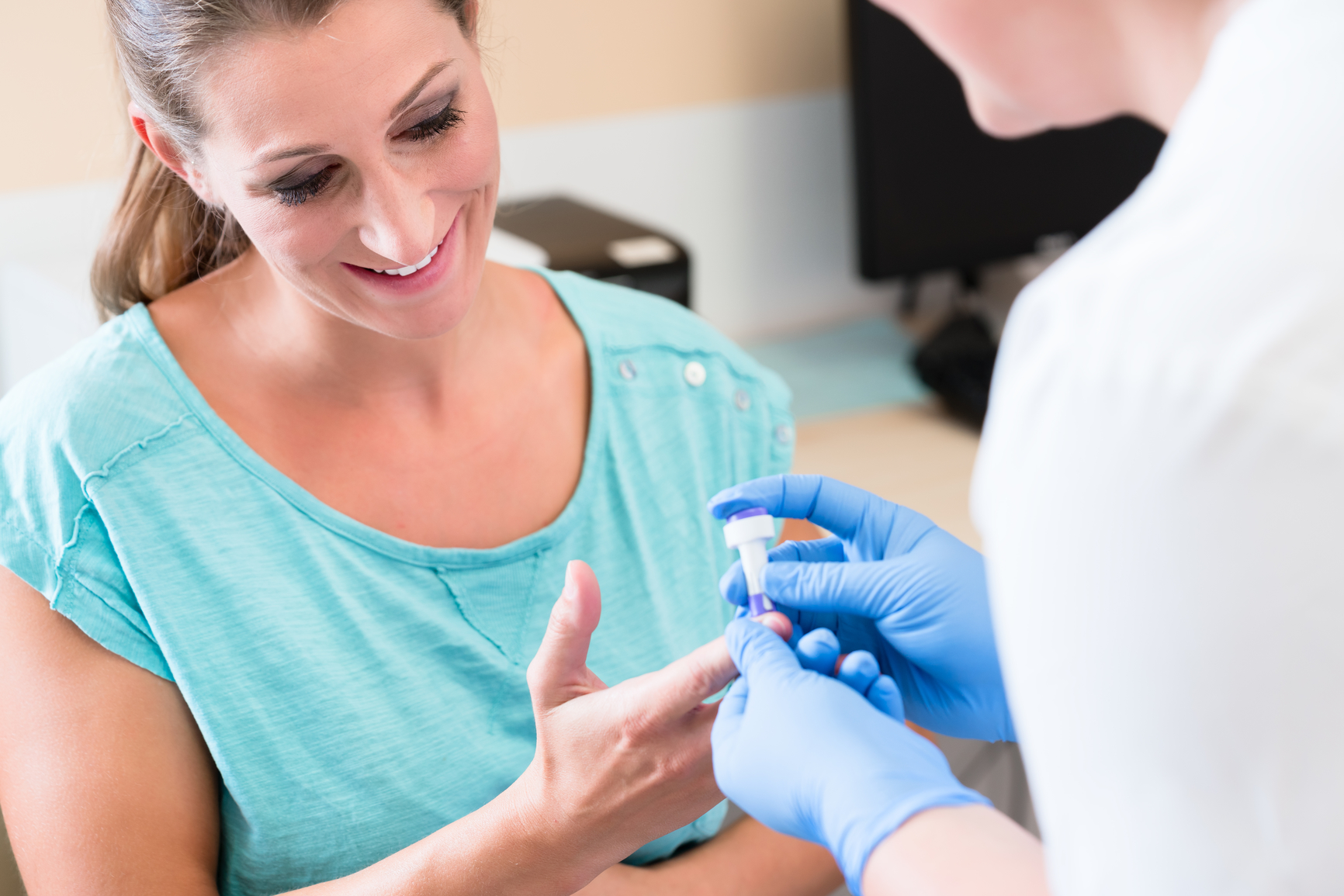
If you have any of the above risk factors, you will be offered a glucose test during pregnancy. This may be a simple blood test in early pregnancy and/or a glucose tolerance test when you are between 24 and 28 weeks pregnant.
A Glucose Tolerance Test is a test which measures the amount of sugar in your blood before and after you have taken a sugary drink.
Before the test it is important that you eat normally for the three days before the test. Also, not take any extra exercise the day before the test. You should have nothing to eat or drink after 10.00pm the night before the test, except for water. If you are a smoker it is also important that you do not smoke during the test.
The test will take just over two hours. Therefore, we recommend bringing a book or tablet for entertainment. When you arrive for you test: –
It is important that you do not exercise whilst the test is being performed. At the end of the test you will be able to go home. You may wish to bring a snack with you to have before you leave (at the end of the test).
The bloods are then sent to the laboratory for analysis. The diagnosis of gestational diabetes if made if: –
Your consultant/midwife will contact you with the results of your test as soon as they are available. If you are diagnosed with gestational diabetes, your care will be managed by a consultant and you will receive extra antenatal care.
Most women who develop diabetes in pregnancy have a healthy pregnancy and baby but occasionally gestational diabetes can cause serious problems. Diagnosing and treating gestational diabetes reduces these risks. The most important treatment is a healthy diet and exercise. Gestational diabetes usually improves with these changes for most women, although some women, despite their best efforts require medication.